Like physiotherapists, osteopaths diagnose and treat injury using hands-on manual techniques. These include soft tissue manipulation, orthopaedic and neurological testing as well as massage, stretching muscle groups and spinal adjustments.
At the start of your session they will take a detailed case history and perform a physical examination. This allows them to formulate a diagnosis that takes into account your specific symptoms and medical history.
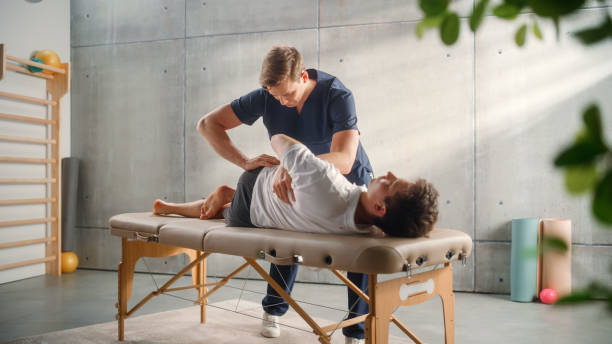
Osteopathy is a gentle hands-on therapy that looks at how the bones, muscles and internal structures of your body work together. It was founded in the late 19th Century by a physician called Andrew Taylor Still, who believed that the manipulation of the musculoskeletal system could treat a wide range of conditions without the negative side effects of drugs. He also believed that structure and function are interrelated, so changes in the musculoskeletal system could influence other systems of the body.
Osteopaths are regulated health practitioners and are trained to treat a wide variety of injuries and conditions including back pain, neck pain, sciatica, headaches, sports-related injuries, joint pain and carpal tunnel syndrome. Patients often find that osteopathic treatments help to alleviate many of the symptoms of their chronic diseases.
A typical osteopathic session in Muscle Joint Bone lasts for 40 to 60 minutes and involves manual techniques such as soft tissue massage, joint manipulation, stretching, muscle energy techniques, cranial osteopathy and visceral osteopathy. Treatments are tailored to each individual patient and a full medical history is taken.
A few high-quality randomised controlled trials (RCTs) have found that osteopathic treatment is effective for non-specific low back pain. However, more research is needed on the effect of specific osteopathic modalities. It would be useful for future RCTs to compare different osteopathic approaches to see which are most effective.
Osteopaths
Osteopaths focus on the neuro-musculoskeletal system – the bones, muscles and nerves that support the body and control movement. They offer musculoskeletal and nervous system assessments, manual therapy, clinical exercise programs, movement and postural assessment, ergonomic assessment and therapeutic needling techniques (dry needling or trigger point therapy).
Osteopathy is based on the principle that the structure of your body is interconnected and that the body has an innate ability to self-regulate and heal. Osteopaths use hands-on skills to optimize the structural alignment of your body, improve its function and assist in the recovery from injury and illness.
Their osteopathic manipulative treatment (OMT) is gentle and safe. It involves gently placing your body into positions that encourage the release of tension and help relieve pain. It also includes soft tissue massage, joint mobilization and craniosacral therapy, a form of touch that addresses the head, neck and spine.
Unlike many other health care practitioners, Balwyn North osteo are licensed to treat a wide range of medical problems. These include respiratory conditions, including asthma and sinus infections; bowel problems, such as irritable bowel syndrome; menstrual disorders; chronic pain, including back and neck pain, headaches and migraines; and arthritis.
A DO may also use OMT to help improve the functioning of your organs, such as your heart, lungs or digestive tract. They are trained to recognize when a patient’s structural imbalance is limiting the flow of blood and oxygen to an organ, causing it to become dysfunctional.
Physiotherapists
Physiotherapists are trained to diagnose and treat injuries and health issues. They are known for helping patients to recover from a range of conditions including back pain, neck pain, and sports injuries. In general, physiotherapists will treat the presenting complaint but they will also educate their clients to prevent recurrence and provide advice on exercise programs.
Originally, the practice of osteopathy was developed in the 19th century by Andrew Taylor Still. It is based on the principle that the body functions as one unit and that no part of the body works independently. Abnormalities in any area can influence and disadvantage other areas. Therefore, osteopathic treatment is based on boosting the body’s self-healing mechanisms to overcome illness and disease.
Osteopaths have a much wider skill set and are more likely to use spinal manipulation compared to physiotherapists, who are more focused on treating the specific area of injury. However, both practitioners are well versed in manual therapy and will be able to assess your symptoms and come up with a treatment plan that is best for you.
When you visit a Balwyn North physio, they will take into account your current symptoms and lifestyle to create a personalised approach to managing them. They will teach you exercises to help you manage your injury at home and work with you to improve your overall mobility, balance and posture.
What is the Difference?
Despite the stereotypical impression that osteopaths only crack bones and physiotherapists only strap ankles, both disciplines have more similarities than differences. Both professions use manual techniques (massage, manipulation, articulation and mobilisation) to improve blood circulation and movement and relieve pain. Both professions also focus on the musculoskeletal system and both have a holistic approach based on the principle that the body has self-healing mechanisms.
Osteopaths look at the whole body to locate areas of strain and dysfunction, a common cause of aches and pains. This is because well-being relies on the musculoskeletal and visceral systems working in harmony with each other.
When assessing the root causes of your ache or pain, osteopaths will take your medical history and perform a full postural and gait assessment. They will then gently manipulate your joints and soft tissues to improve your mobility, reduce inflammation and improve the function of your muscles, tendons and ligaments.
Physiotherapists will also assess your ache or pain and take your medical history into account to identify the root cause of the issue. They will then use a variety of methods to help relieve pain and increase blood flow and nerve supply including manual therapy, exercise, acupuncture, electrical stimulation and education. Physiotherapists may specialise in certain areas such as women’s health, sports injury or spinal injuries.